What is commonhold? Commonhold for residential blocks of flats explained
Commonhold refers to a type of property ownership that was introduced by the Commonhold and Leasehold Reform Act 2002, but not made mandatory. It provides an alternative to leasehold ownership, which is the traditional form of property ownership for residential flats in the UK.
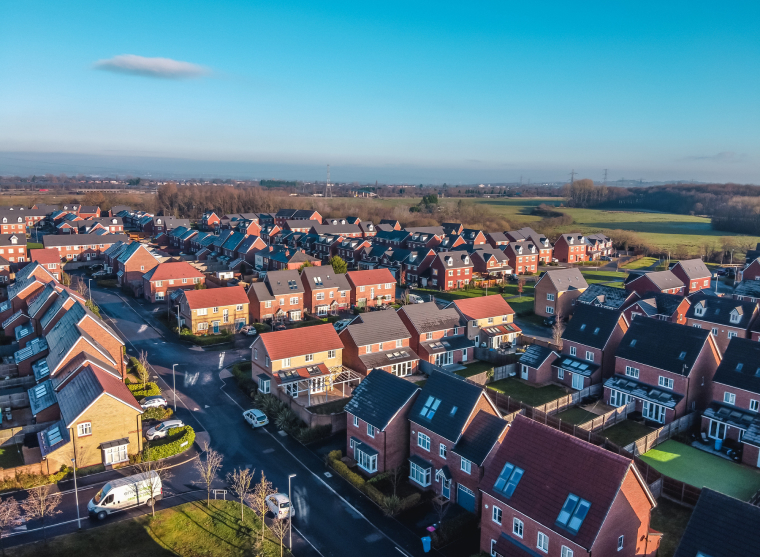
Under a commonhold arrangement, individual unit owners have freehold ownership of their specific flat or apartment within a building, as well as a shared ownership of the common areas and facilities of the building or development. Common areas may include hallways, staircases, gardens, and other communal spaces.
The key feature of commonhold is that it allows unit owners to collectively manage the shared areas and make decisions regarding the management and maintenance of the property. This is typically achieved through the establishment of a commonhold association, which is made up of the unit owners. The association is responsible for the day-to-day management and decision-making related to the commonhold property.
Commonhold provides a more democratic and transparent form of ownership compared to leasehold, as unit owners have a direct say in the management of the property. It also offers greater security and control over the property, as commonhold ownership does not involve leasehold arrangements with ground rents, lease terms, and potential lease extensions.
Social
Valuation Services provided by Ringley's Valuation Team
Block Management Packages
Legal Services provided by Ringley Law
Building Surveying Services
Meet our Expert Property Commentators
What is commonhold? Commonhold for residential blocks of flats explained
Commonhold refers to a type of property ownership that was introduced by the Commonhold and Leasehold Reform Act 2002, but not made mandatory. It provides an alternative to leasehold ownership, which is the traditional form of property ownership for residential flats in the UK.
Under a commonhold arrangement, individual unit owners have freehold ownership of their specific flat or apartment within a building, as well as a shared ownership of the common areas and facilities of the building or development. Common areas may include hallways, staircases, gardens, and other communal spaces.
The key feature of commonhold is that it allows unit owners to collectively manage the shared areas and make decisions regarding the management and maintenance of the property. This is typically achieved through the establishment of a commonhold association, which is made up of the unit owners. The association is responsible for the day-to-day management and decision-making related to the commonhold property.
Commonhold provides a more democratic and transparent form of ownership compared to leasehold, as unit owners have a direct say in the management of the property. It also offers greater security and control over the property, as commonhold ownership does not involve leasehold arrangements with ground rents, lease terms, and potential lease extensions.
Valuation Services provided by The Ringley Group
Meet our Expert Property Commentators